Understanding The Health Impacts Of Microplastics On The Human Body
Microplastics, tiny polymeric particles of sub-millimetric dimensions, have insidiously permeated an extensive array of environmental substrata. These particles, either the residua of macroscopic polymeric materials undergoing ablation or intentionally synthesized for inclusion in many commercial products, exemplify the pernicious pervasiveness of anthropogenic contaminants. The relentless accretion of these particulates has precipitated many ecotoxicological perturbations, accentuating the necessity for a more meticulous explanation of the potential ramifications on human health and ecological stability.
Vectors Of Human Exposure To Microplastics
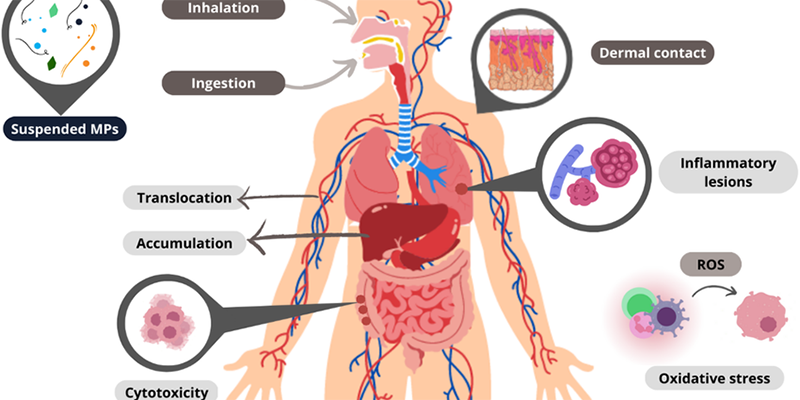
Humans are inadvertently exposed to microplastics through an assortment of exposure vectors. These include inhaling aerosolized particles, ingesting adulterated alimentary and potable resources, and dermal contact with products permeated by microplastics. The insidious omnipresence of these particulates in quotidian life underscores the necessity of thoroughly comprehending microplastic health risks.
The Confluence Of Microplastics And Environmental Toxins
Microplastics exhibit a pernicious propensity to serve as vectors for ancillary toxicants. They possess a penchant for adsorbing and amplifying the impact of environmental toxins, including persistent organic pollutants (POPs) and heavy metals, from their surrounding milieu. Upon ingestion, these toxophoric microplastics may release their deleterious cargo within the human organism, thereby exacerbating microplastics' health risks. The protracted bioaccumulation of both microplastics and their concomitant toxicants incites trepidation regarding the potential for chronic pathologies, including carcinogenesis and neurodegenerative syndromes.
Microplastics In The Human Physiology: Contemporary Insights
Gastrointestinal Integrity And Microbiome Perturbation
The ingestion of microplastics manifests significant health risks, particularly concerning gastrointestinal integrity. Once internalized, microplastics can precipitate dysbiosis within the gut microbiome, engendering inflammatory responses, impairing gut functionality, and augmenting the permeability of the intestinal epithelium. This phenomenon, colloquially termed "leaky gut," permits pernicious substances to translocate into the systemic circulation, inciting widespread inflammation and harmful health outcomes. Microplastics' effects on food health are notably perturbing, as they constitute a direct conduit of exposure with potentially grievous ramifications for digestive health.
Respiratory System Encumbrances
The inhalation of aerosolized microplastics is a burgeoning concern, given the potential for these particles to become entrapped within the pulmonary architecture. This can precipitate respiratory disorders such as asthma, bronchitis, and potentially pulmonary carcinomas. The environmental toxins associated with inhaled microplastics may further exacerbate these respiratory afflictions, particularly within urban environments characterized by heightened pollution indices.
Cardiovascular And Neurovascular Complications
Emergent research intimates that microplastics may also pose insidious threats to the cardiovascular and neurovascular systems. Upon breaching the systemic circulation, these particulates may disseminate to various organs, precipitating inflammatory responses and oxidative stress. The impact of environmental toxins inherent to microplastics further complicates this issue, as these toxicants may induce cytotoxicity and disrupt homeostatic physiological processes. The systemic distribution of microplastics raises disconcerting queries regarding the microplastic health risks pertinent to cardiovascular pathologies, cerebrovascular accidents, and neurological disorders.
Ameliorating The Health Consequences Of Microplastics
Mitigating Microplastic Exposure
Given the pervasiveness of microplastics, the attenuation of exposure constitutes a formidable yet imperative undertaking. Strategies to mitigate microplastic health risks include:
- Circumventing products embedded with microbeads, such as specific personal care products and household cleaners.
- Promoting legislative measures that curtail plastic manufacturing and advocate for the proliferation of biodegradable alternatives.
- Diminishing reliance on single-use plastics to curtail the proliferation of plastic residue in the environment.

The Imperative For Rigorous Research And Stringent Regulation
Augmented research endeavours are indispensable to fully delineate the effects of microplastics on food health effects and the overarching environmental toxins impact. Contemporary scholarly investigations continue to unravel the intricacies of these health hazards, underscoring the necessity for regulatory authorities to prioritize research funding and formulate stringent guidelines to protect public health. As our comprehension of microplastic health risks deepens, the necessity for targeted regulations that address the sources of microplastic pollution and restrict human exposure becomes increasingly manifest.
The Role Of Public Edification
Public edification initiatives play a pivotal role in diminishing the impact of environmental toxins by raising awareness about the sources of microplastics and proposing strategies to reduce exposure. By making informed decisions, consumers can engender demand for safer, plastic-free products and endorse initiatives to curtail microplastic contamination.
Ecological Ramifications Of Microplastics
Microplastics possess a pernicious omnipresence that transcends mere human health concerns, insidiously infiltrating and compromising the integrity of ecological networks. These minuscule particulates surreptitiously impair the biological homeostasis of aquatic organisms, instigating a cascade of harmful effects that reverberate through the trophic hierarchy. Thus, microplastic health risks are amplified as these contaminants bioaccumulate in higher trophic levels, including apex predators.
Bioaccumulation And Biomagnification
The insidious nature of bioaccumulation lies in the gradual sequestration of microplastics and their accompanying environmental toxins' impact within the somatic tissues of organisms over protracted temporal scales. These toxicants remain ensconced within lipid-rich tissues, exerting latent effects that exacerbate with time. As trophic interactions progress, the process of biomagnification amplifies these microplastics' health risks, as each successive predator inherits an increasingly concentrated toxic load, culminating in heightened exposure risks for top-tier consumers, particularly humans.
Endocrine Disruption In Wildlife And Humans
Microplastics frequently act as vectors for endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs), which possess an unnerving propensity to perturb the finely tuned hormonal equilibria in both faunal and human physiologies. Phthalates and bisphenol A (BPA), ubiquitous EDCs associated with microplastics, have the potential to either mimic or antagonize endogenous hormones, thereby inducing a spectrum of pathophysiological aberrations.
Impact Of Microplastics On Reproductive Health
Fertility And Developmental Concerns
Microplastics inhaled and consumed herald a myriad of insidious repercussions for reproductive health. The environmental toxins associated with these particulates manifest in attenuated fecundity and perturbations in embryonic development. These reproductive detriments may materialize as oligomenorrhea, teratozoospermia, and embryonic teratogenesis. The intergenerational transmission of these microplastic health risks necessitates an expansive investigation of the latent ramifications of sustained microplastic exposure, especially in human reproductive viability.
Placental And Fetal Exposure
Microplastics exhibit an alarming propensity to traverse the placental interface, thereby compromising fetal development by introducing xenobiotics and particulates into the intrauterine environment. This transplacental migration may precipitate intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR), preterm parturition, and congenital malformations. The intersection of microplastics in food health effects with fetal development underscores the imperative for a nuanced understanding of how maternal dietary habits and environmental exposures synergistically contribute to these prenatal adversities.
Conclusion
The health risks engendered by the omnipresence of microplastics within our environment represent an insidious and escalating menace. As ongoing scientific investigations progressively unravel the harmful effects of microplastics in food and the implications of environmental toxins, the necessity for swift and resolute intervention becomes undeniable. Curtailing exposure, amplifying research endeavours, and fortifying public consciousness are indispensable measures in confronting the potential health repercussions of microplastics on human physiology.